What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Why Should You Care?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a common yet serious sleep disorder that affects millions of people. It occurs when the airway becomes partially or completely blocked during sleep, causing repeated interruptions in breathing. While snoring may be one of the more obvious signs, the effects of OSA extend far beyond disrupting your sleep—and they can significantly impact your overall health.
In this blog post, we’ll explain what OSA is, why it matters, and how you can take steps to protect your health.
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
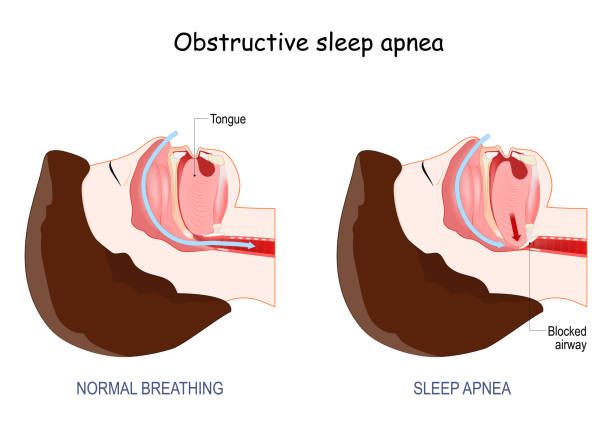
Obstructive Sleep Apnea happens when the muscles in the throat relax too much during sleep, narrowing or closing the airway. This results in brief pauses in breathing, often followed by gasping or choking.
These interruptions can happen dozens—or even hundreds—of times a night, disrupting your sleep cycles and lowering oxygen levels in your blood.
Key Symptoms of OSA:
- Loud, persistent snoring
- Gasping, choking, or pauses in breathing during sleep
- Excessive daytime fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating or memory problems
- Irritability or mood swings
- Morning headaches or dry mouth
Why Should You Care About OSA?
OSA is more than just a nuisance—it’s a serious health condition with far-reaching consequences.
1. Heart Health Risks
Untreated OSA increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. The repeated drops in oxygen levels put significant strain on your cardiovascular system.
2. Cognitive Decline
OSA disrupts restorative sleep, which is crucial for memory and brain function. Over time, this can lead to memory problems and even dementia.
3. Diabetes and Metabolic Issues
Sleep apnea is closely linked to insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes, as poor sleep impacts how your body processes glucose.
4. Mood and Mental Health
Chronic fatigue caused by OSA can contribute to depression, anxiety, and irritability, significantly affecting your quality of life.
How is OSA Treated?
The good news is that OSA is highly treatable. Options include:
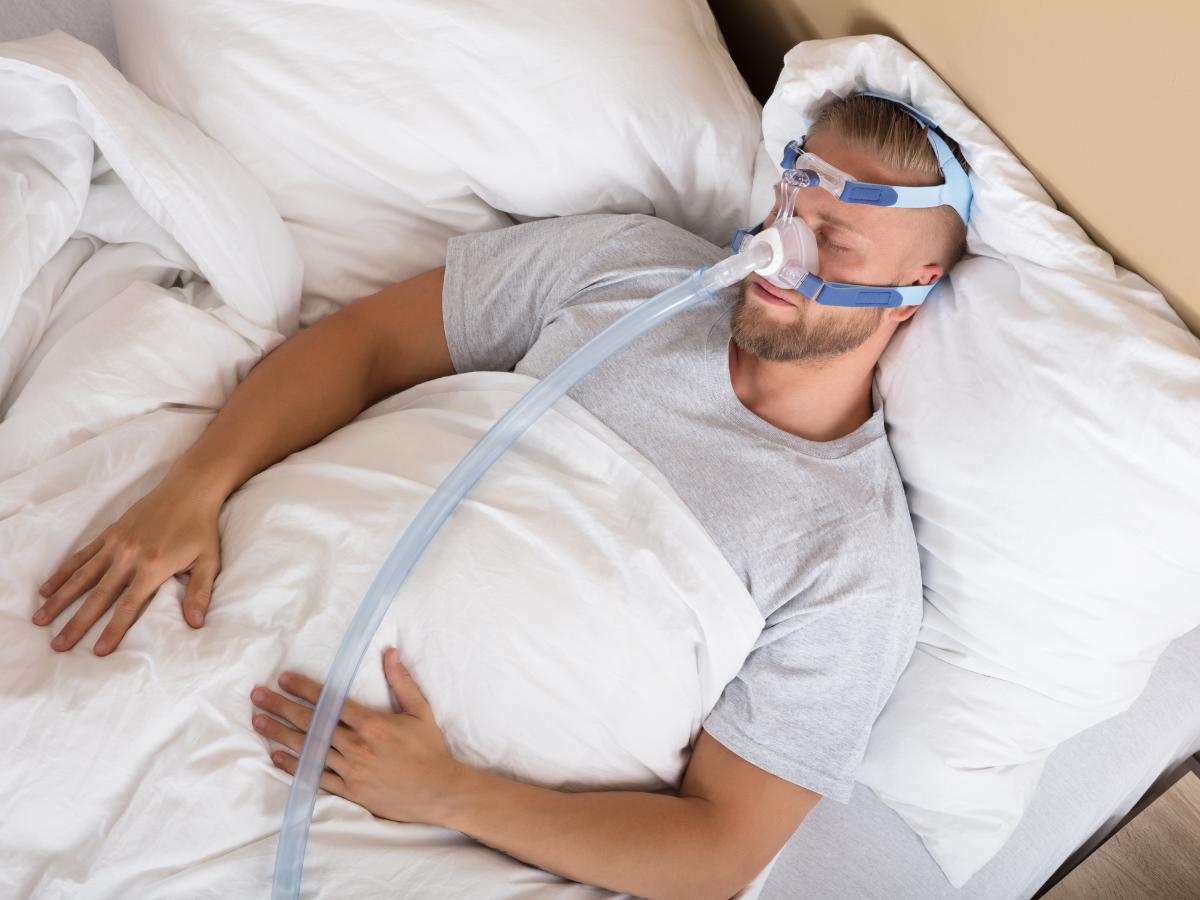
1. CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure)
The most common treatment, CPAP, involves wearing a mask that delivers a constant stream of air to keep your airway open.
2. Oral Appliance Therapy
For mild to moderate cases, a custom-fit oral appliance from your dentist can reposition your jaw and tongue to prevent airway blockages.
3. Lifestyle Changes
- Weight loss can reduce airway obstruction.
- Avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed may help keep your airway open.
When to Seek Help
If you experience loud snoring, daytime fatigue, or other symptoms of OSA, it’s time to get evaluated. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve your quality of life and protect you from serious health complications.
Take the First Step Toward Better Sleep
Obstructive Sleep Apnea is a condition you can’t afford to ignore. If you suspect you have OSA, contact our office today. We offer at-home sleep testing and customized treatment options, including oral appliance therapy, to help you achieve restful, healthy sleep.